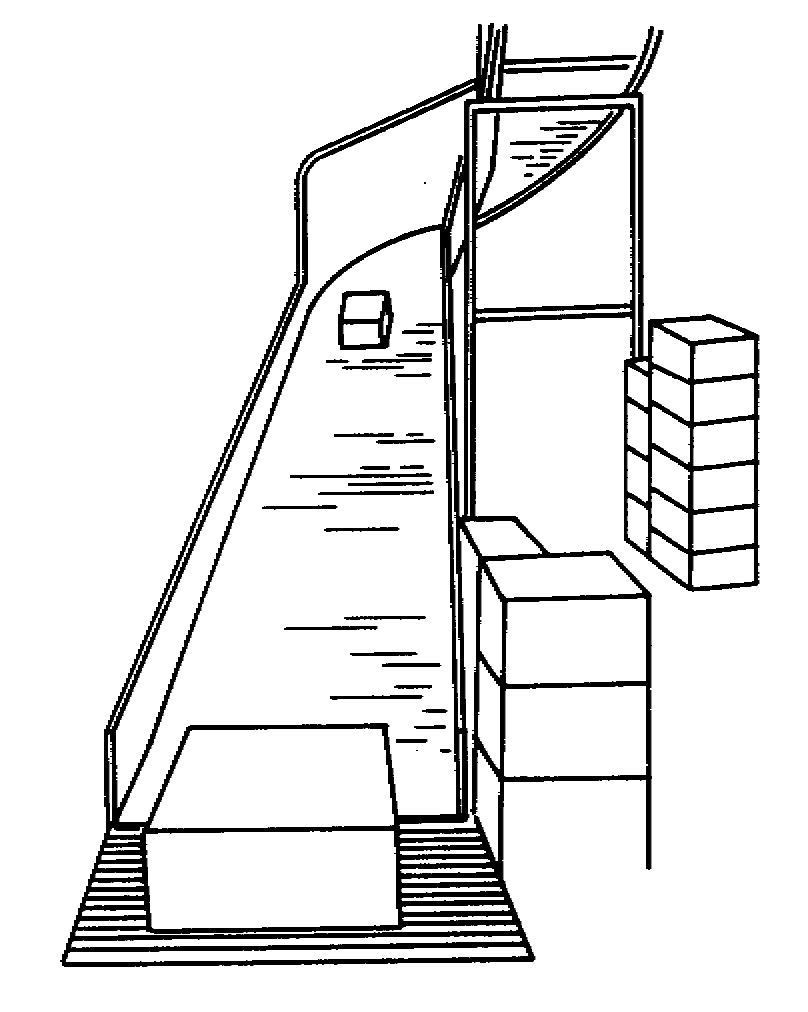
 Unit/Bulk
+ On-Floor + Accumulate
Unit/Bulk
+ On-Floor + AccumulateConveyors are used to move materials over a fixed path.
Conveyors are used:
Conveyors can be classified in different ways:
 Unit/Bulk
+ On-Floor + Accumulate
Unit/Bulk
+ On-Floor + Accumulate
Inexpensive
Used to link two handling devices
Used to provide accumulation in shipping areas
Used to convey items between floors
Difficult to control position of the items
| Top |
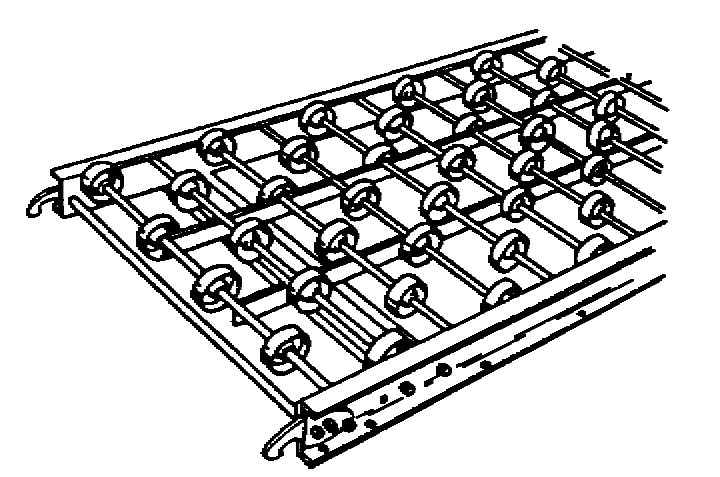
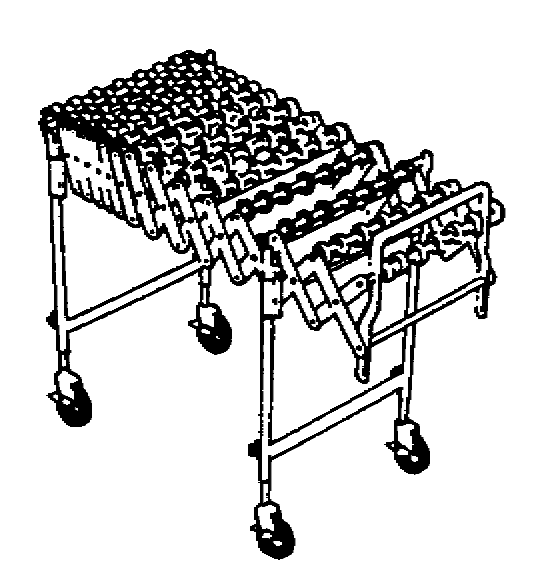 Unit +
On-Floor + Accumulate
Unit +
On-Floor + Accumulate
Uses a series of skatewheels mounted on a shaft (or axle), where spacing of the wheels is dependent on the load being transported
Slope for gravity movement depends on load weight
More economical than the roller conveyor
For light-duty applications
Flexible, expandable versions available
| Top |
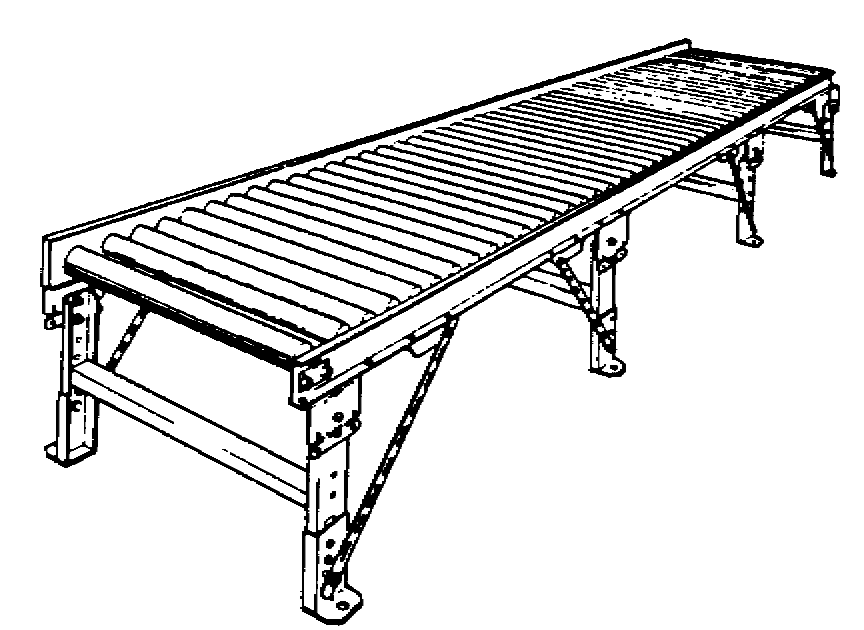
Unit + On-Floor + Accumulate
May be powered (or live) or nonpowered (or gravity)
Materials must have a rigid riding surface
Minimum of three rollers must support smallest loads at all times
Tapered rollers on curves used to maintain load orientation
 Alternative to wheel conveyor
Alternative to wheel conveyor
For heavy-duty applications
Slope for gravity movement depends on load weight
For accumulating loads
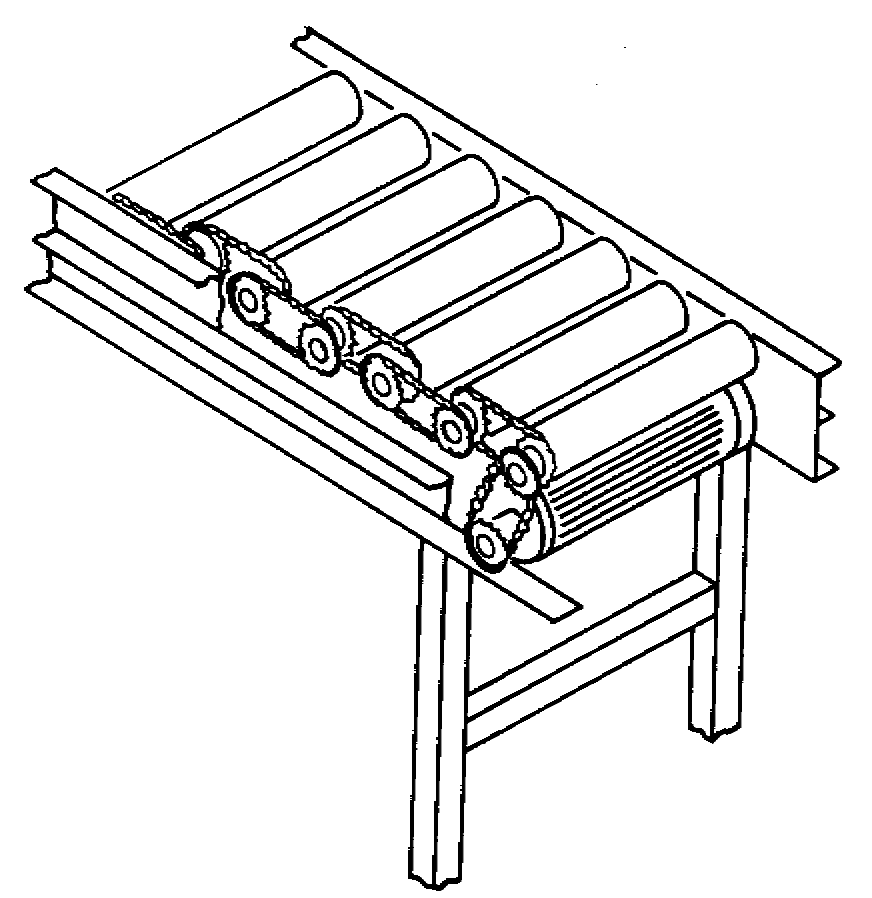 Belt or chain driven
Belt or chain driven
Force-sensitive transmission can be used to disengage rollers for accumulation
For accumulating loads and merging/sorting operations
Provides limited incline movement capabilities
| Top |
 Unit
+ In-/On-Floor + No Accumulate
Unit
+ In-/On-Floor + No Accumulate
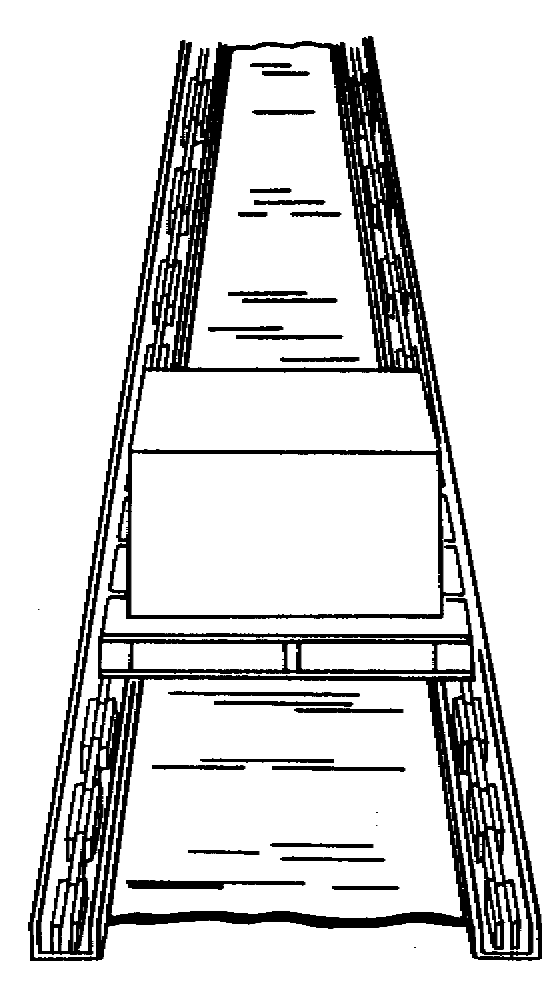
Uses one or more endless chains on which loads are carried directly
Parallel chain configuration used to transport pallets
Vertical chain conveyor used for continuous high-frequency vertical transfers
(cf. vertical conveyor used for low-frequency intermittent transfers)
| Top |
 Unit + In-/On-Floor + No Accumulate
Unit + In-/On-Floor + No Accumulate
Uses discretely spaced slats connected to a chain
Unit being transported retains its position (like a belt conveyor)
Orientation and placement of the load is controlled
Used for heavy loads or loads that might damage a belt
Bottling and canning plants use flat chain or slat conveyors because of wet conditions, temperature, and cleanliness requirements
Tilt slat conveyor used for sortation
| Top |
 Unit + On-Floor + No Accumulate
Unit + On-Floor + No Accumulate
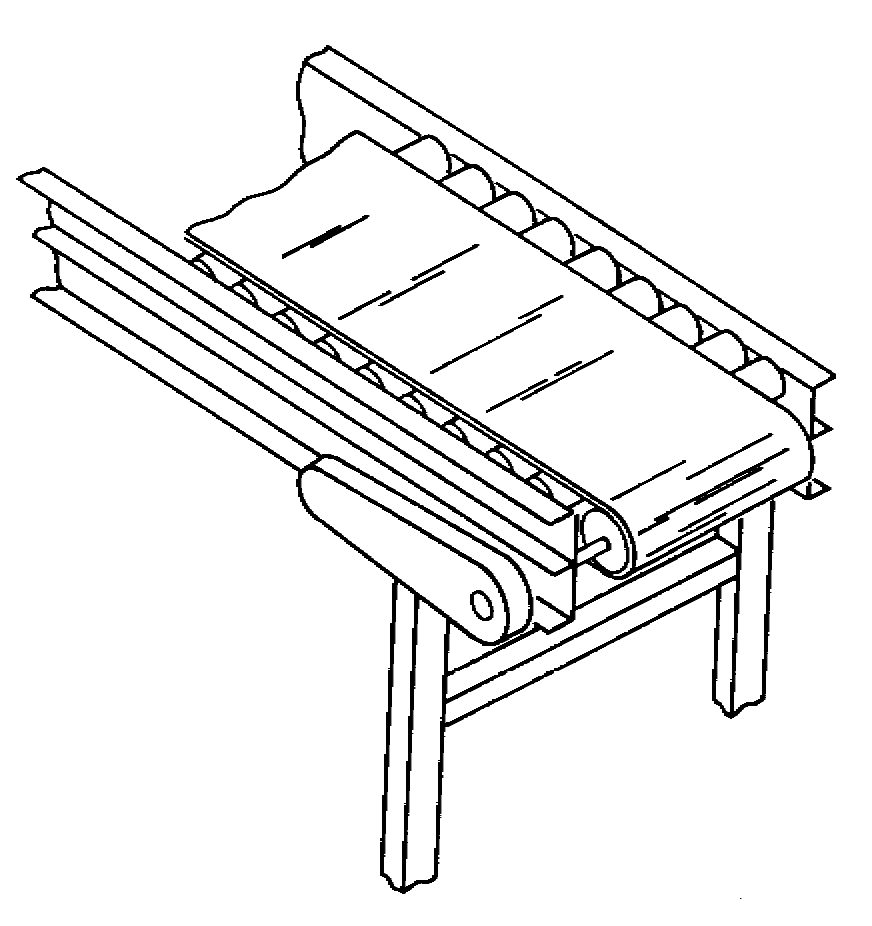
For transporting light- and medium-weight loads between operations, departments, levels, and buildings
When an incline or decline is required
Provides considerable control over the orientation and placement of the load.
No smooth accumulation, merging, and sorting on the belt
The belt is roller or slider bed supported; the slider bed is used for small and irregularly shaped items
In 1957, B.F. Goodrich, Co. patented the Möbius strip for conveying hot or abrasive
substances in order to have "both" sides wear equally 14
| Top |
 Bulk + On-Floor
Bulk + On-Floor
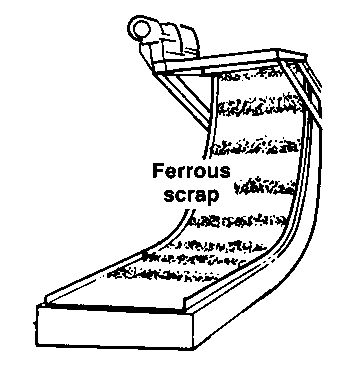
A steel belt and either a magnetic slider bed or a magnetic pulley is used
To transport ferrous materials vertically, upside down, and around corners
| Top |
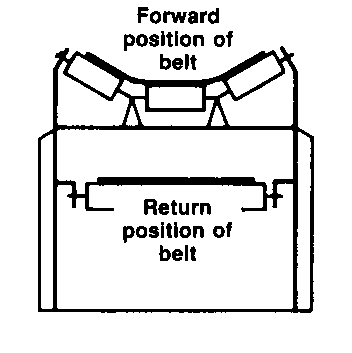 Bulk + On-Floor
Bulk + On-Floor
Used to transport bulk materials
When loaded, the belt conforms to the shape of the troughed rollers and idlers
| Top |
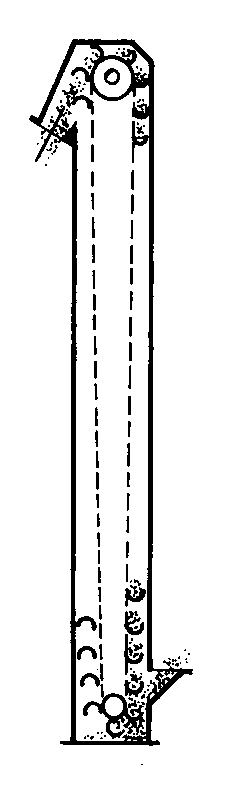 Bulk
+ On-Floor
Bulk
+ On-Floor
Used to move bulk materials in a vertical or inclined path
Buckets are attached to a cable, chain, or belt
Buckets are automatically unloaded at the end of the conveyor run
| Top |
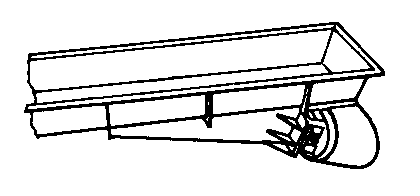 Bulk + On-Floor
Bulk + On-Floor
Consists of a trough, bed, or tube
Vibrates at a relatively high frequency and small amplitude in order to convey individual units of products or bulk material
Can be used to convey almost all granular, free-flowing materials
An Oscillating Conveyor is similar in construction, but vibrates at a lower
frequency and larger amplitude (not as gentle) in order to convey larger objects such as
hot castings
| Top |
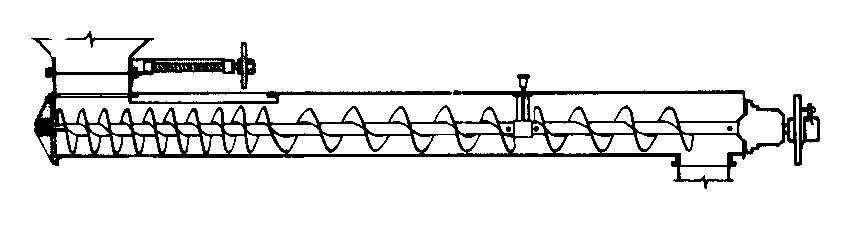 Bulk
+ On-Floor
Bulk
+ On-Floor
Consists of a tube or U-shaped stationary trough through which a shaft-mounted helix revolves to push loose material forward in a horizontal or inclined direction
One of the most widely used conveyors in the processing industry
Many applications in agricultural and chemical processing
Water screw developed circa 250 BC by Archimedes
| Top |
Bulk/Unit + Overhead
Can be used for both bulk and unit movement of materials
Air pressure is used to convey materials through a system of vertical and horizontal tubes
Major advantages are that material is completely enclosed and it is easy to implement turns and vertical moves
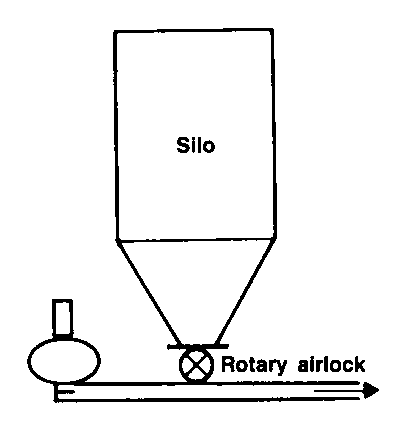 Moves a mixture of air and solid
Moves a mixture of air and solid
Push (positive pressure) systems push material from one entry point to several discharge points
Pull (negative pressure or vacuum) systems move material from several entry points to one discharge point
Push-pull systems are combinations with multiple entry and discharge points
 Carriers are used to transport items or paperwork (e.g., money from drive-in
stalls at banks)
Carriers are used to transport items or paperwork (e.g., money from drive-in
stalls at banks)
| Top |
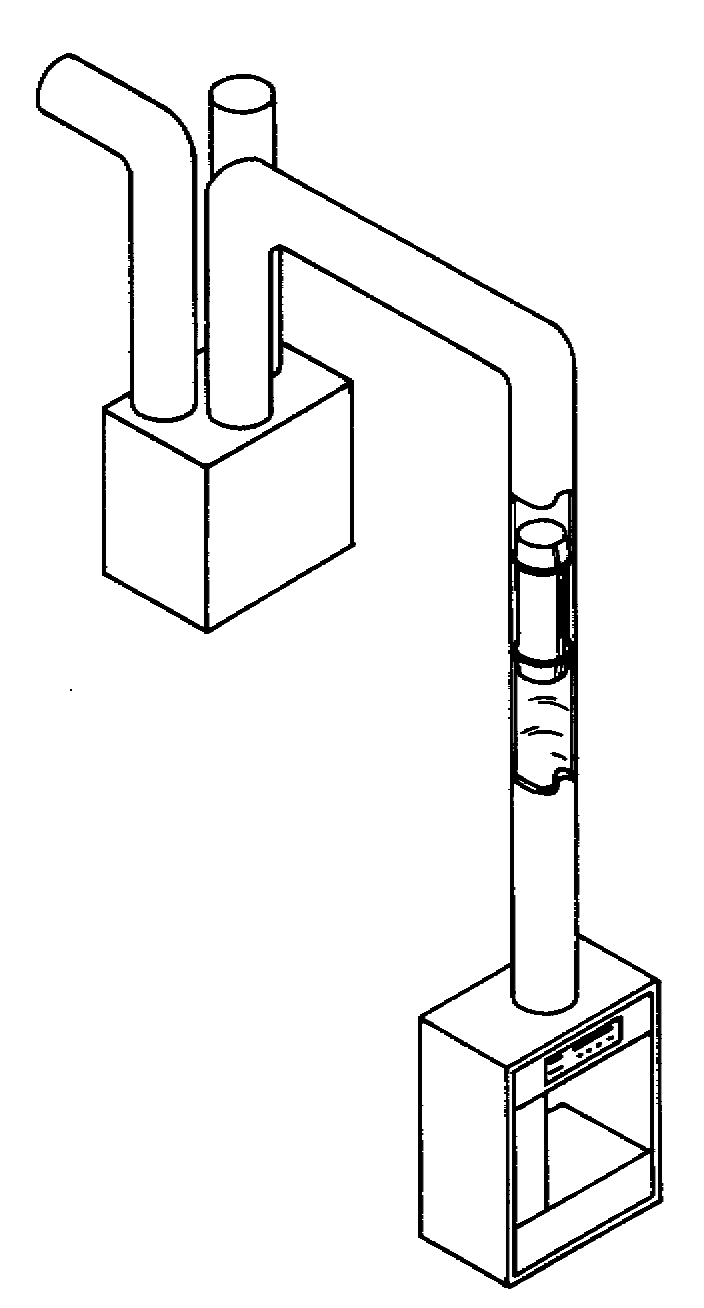
Unit + On-Floor + No Accumulate
Used for low-frequency intermittent vertical transfers (cf. vertical chain conveyor can be used for continuous high-frequency vertical transfers
 Carrier used to raise or lower a load to different levels of a facility
(e.g., different floors and/or mezzanines)
Carrier used to raise or lower a load to different levels of a facility
(e.g., different floors and/or mezzanines)
Differs from a freight elevator in that it is not designed or certified to carry people
Can be manually or automatically loaded and/or controlled and can interface with
horizontal conveyors
 Utilizes gravity-actuated carrier to lowering loads, where the load overcomes
the magnitude of a counterweight
Utilizes gravity-actuated carrier to lowering loads, where the load overcomes
the magnitude of a counterweight
Can only be used to lower a load
Alternative to a chute conveyor for vertical "drops" when load is fragile and/or space is limited
Can be manually or automatically loaded and/or controlled and can interface with
horizontal conveyors
| Top |
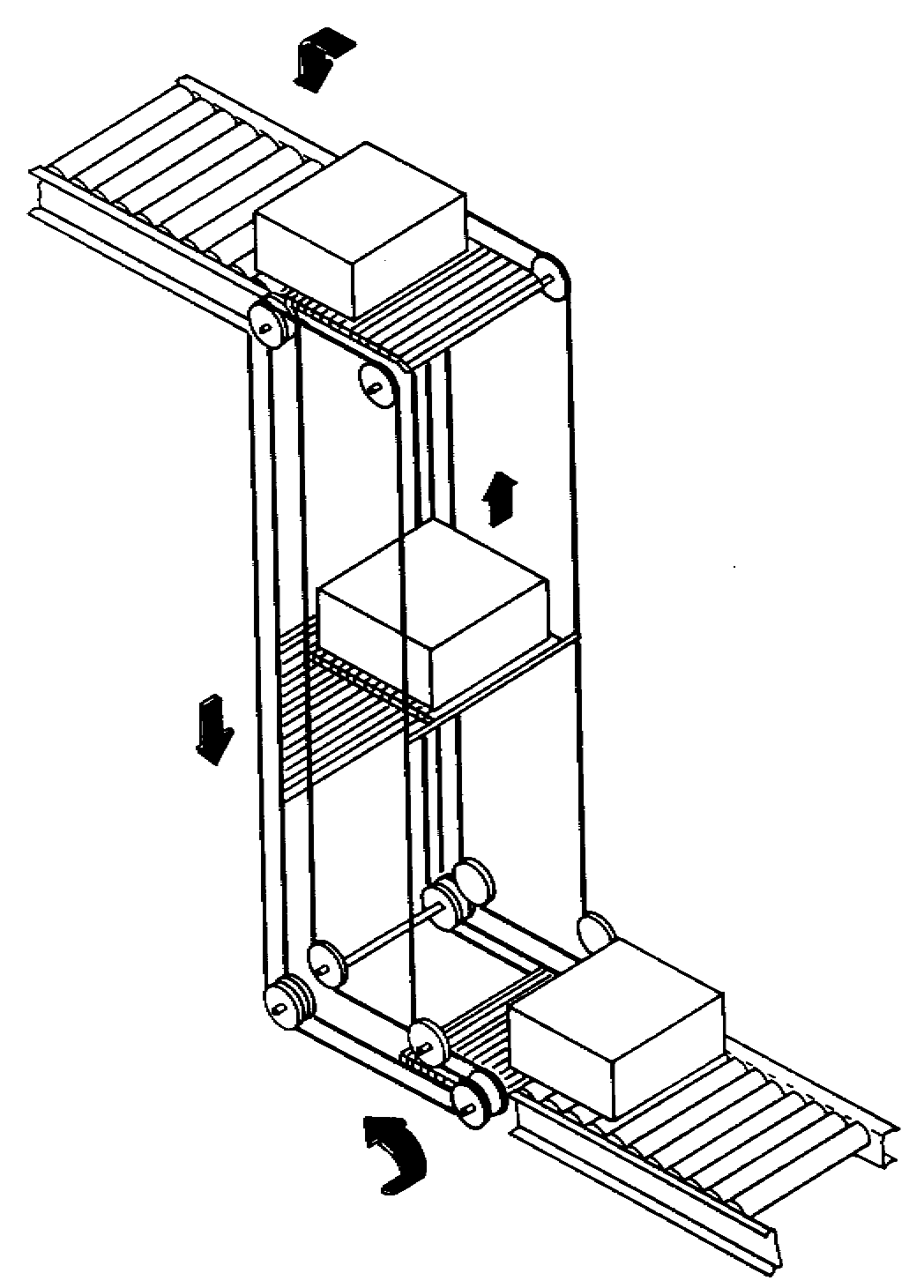
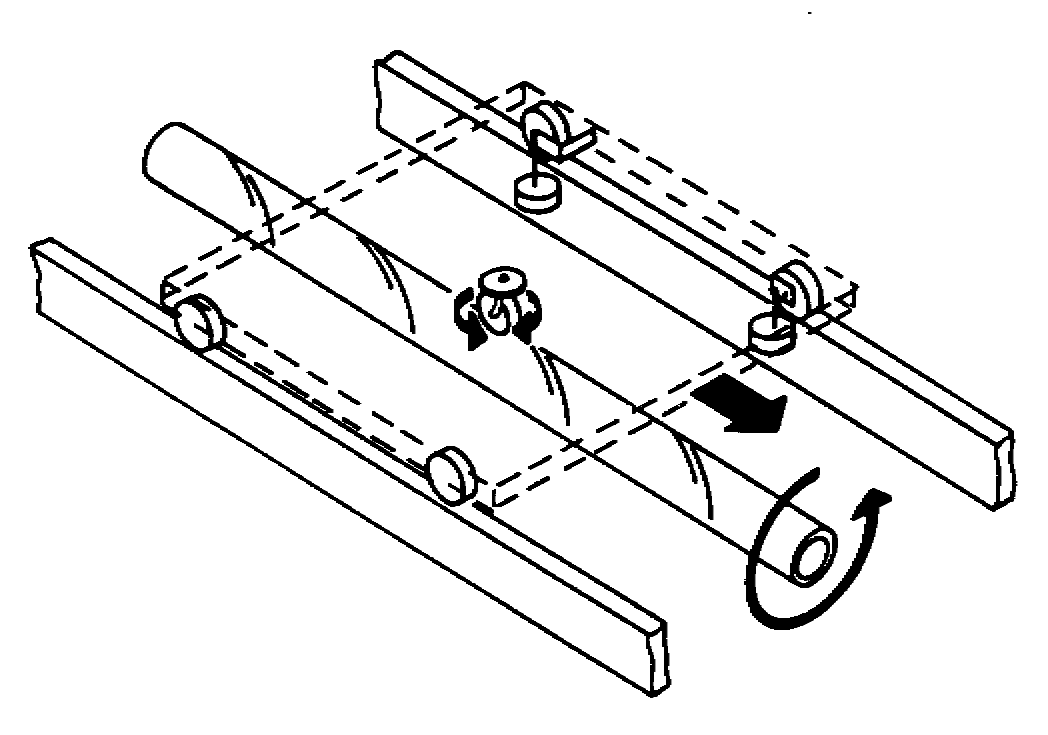 Unit + In-Floor + Accumulate
Unit + In-Floor + Accumulate
Used to transport carts along a track
Carts are transported by a rotating tube
Connected to each cart is a drive wheel that rests on the tube and that is used to vary the speed of the cart (by varying the angle of contact between the drive wheel and the tube)
Carts are independently controlled
Accumulation can be achieved by maintaining the drive wheel parallel to the tube
| Top |
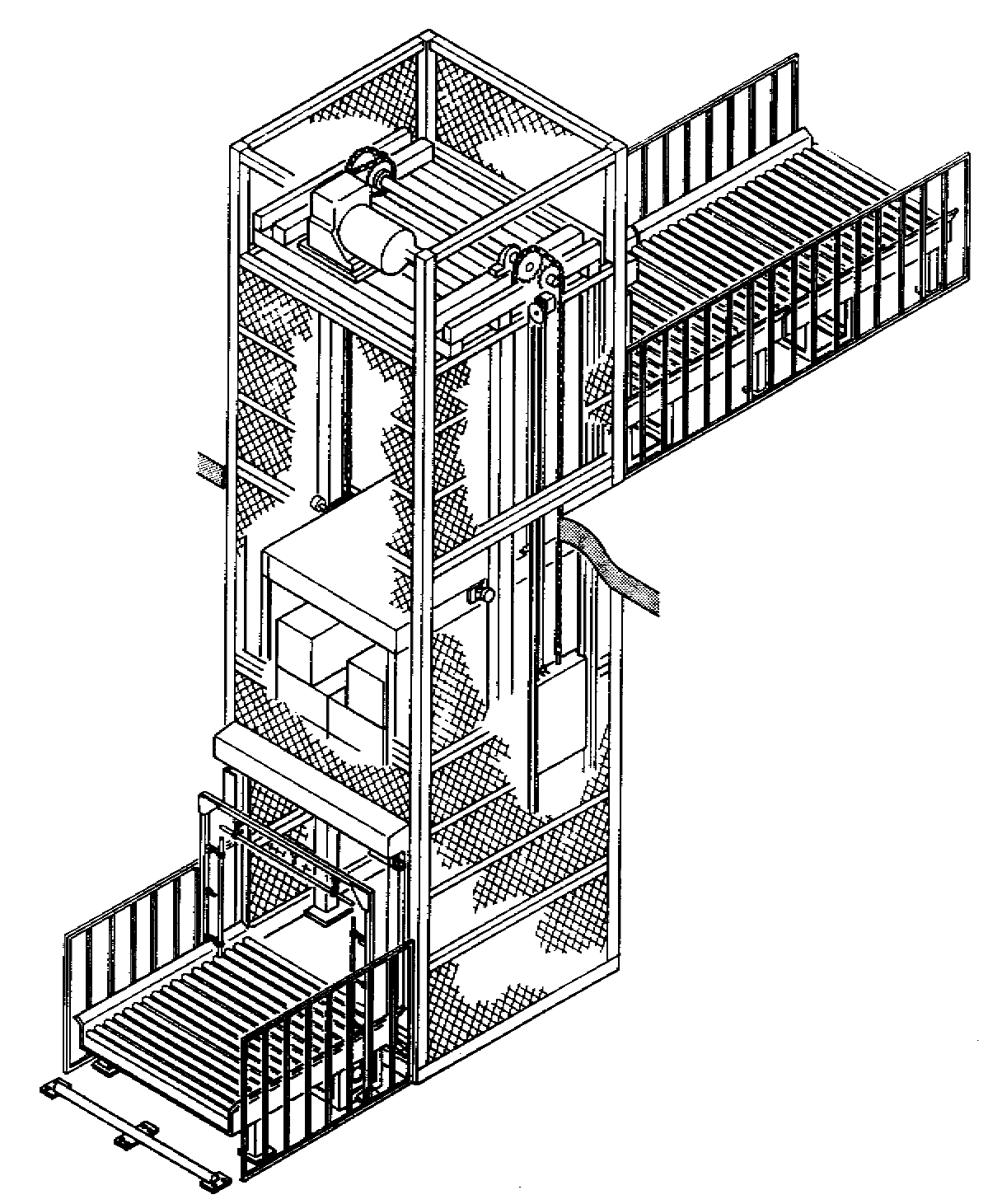
 Unit
+ In-Floor + Accumulate
Unit
+ In-Floor + Accumulate
Uses towline to provide power to wheeled carriers such as trucks, dollies, or carts that move along the floor
Used for fixed-path travel of carriers (each of which has variable path capabilities when disengaged from the towline)
Towline can be located either overhead, flush with the floor, or in the floor
Selector-pin or pusher-dog arrangements can be used to allow automatic switching (power or spur lines)
Generally used when long distance and high frequency moves are required
| Top |
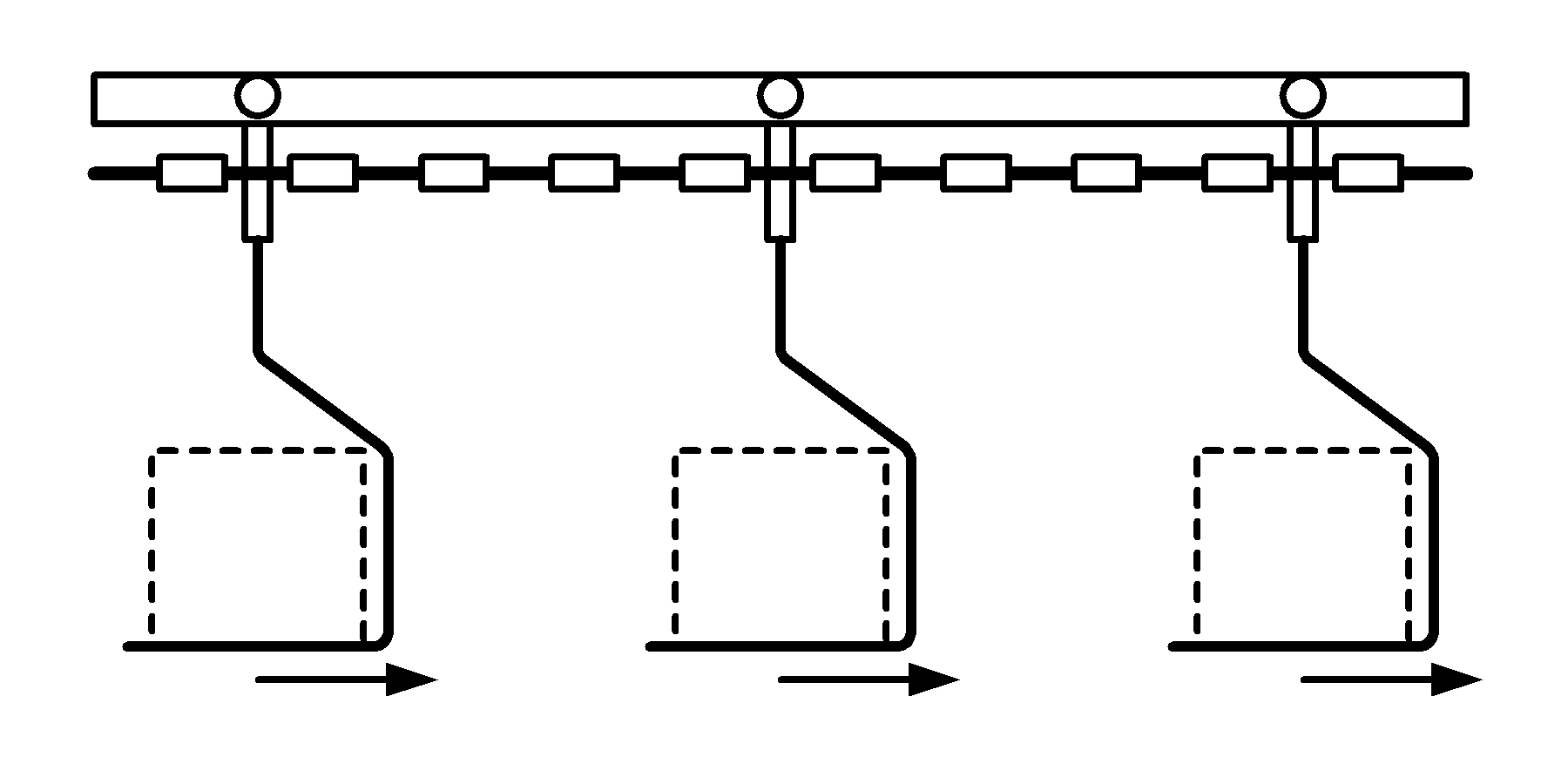
.gif)
Unit + Overhead + No Accumulate
Uses a series of trolleys supported from or within an overhead track
Trolleys are equally spaced in a closed loop path and are suspended from a chain
Carriers are used to carry multiple units of product
Does not provide for accumulation
Commonly used in processing, assembly, packaging, and storage operations
| Top |
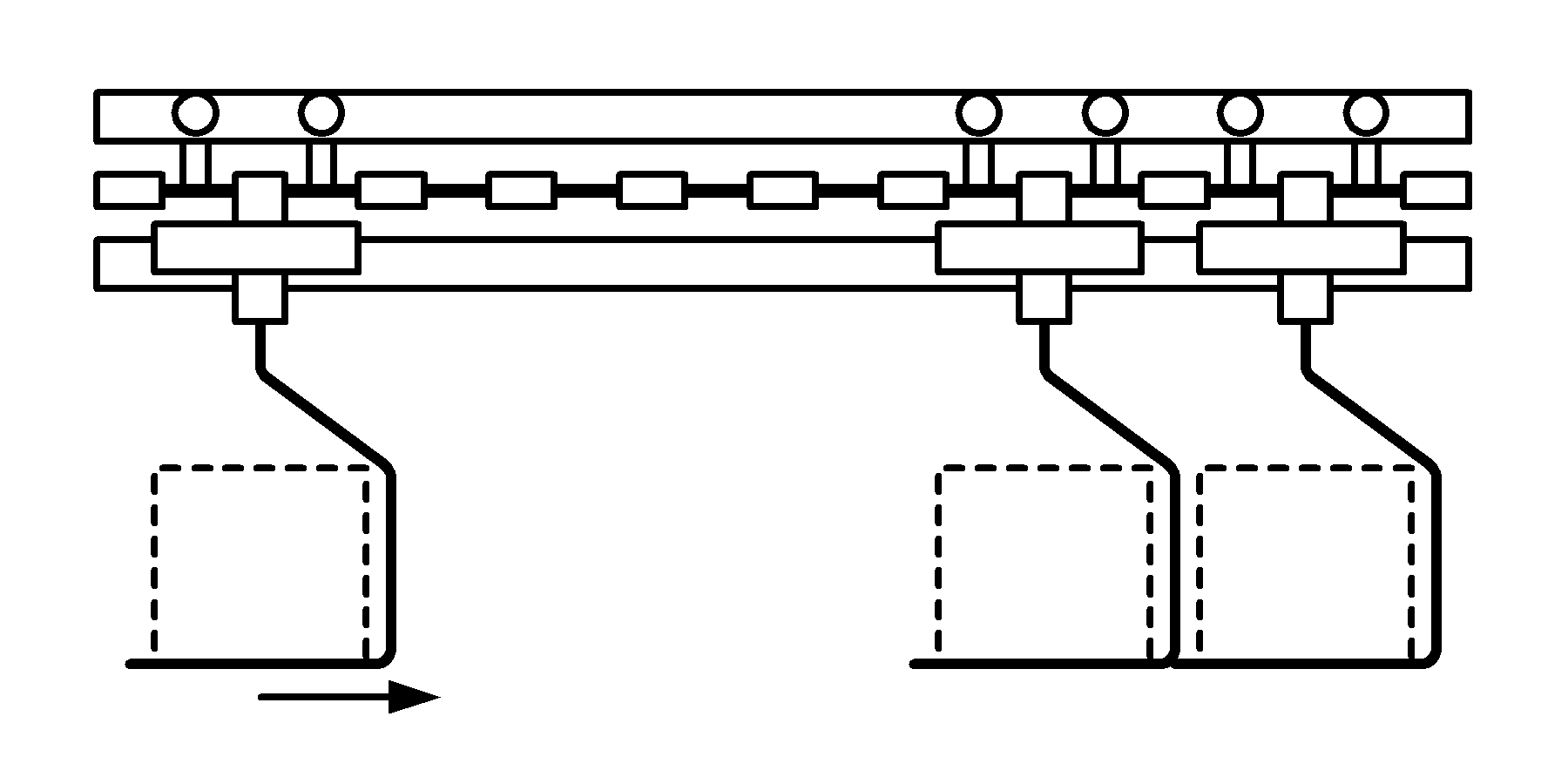
.gif)
Unit + Overhead/On-Floor + Accumulate
Similar to trolley conveyor due to use of discretely spaced carriers transported by an overhead chain; however, the power-and-free conveyor uses two tracks: one powered and the other nonpowered (or free)
Carriers can be disengaged from the power chain and accumulated or switched onto spurs
Termed an Inverted Power-and-Free Conveyor when tracks are located on the floor
| Top |
.gif)
Unit + Overhead + Accumulate
Overhead single track (i.e., mono-rail) or track network on which one or more carriers ride
Carriers: powered (electrically or pneumatically) or nonpowered
Carrier can range from a simple hook to a hoist to an intelligent-vehicle-like device
Single-carrier, single-track monorail similar to bridge or gantry crane
Multi-carrier, track network monorail similar to both a trolley conveyor, except that the carriers operate independently and the track need not be in a closed loop, and a fixed-path automatic guided vehicle (AGV) system, except that it operates overhead
Termed an Automated Electrified Monorail (AEM) system when it has similar control characteristics as an AGV system
| Top |
.gif)
Unit + On-Floor/Overhead
Sortation conveyors are used for merging, identifying, inducting, and separating products to be conveyed to specific destinations
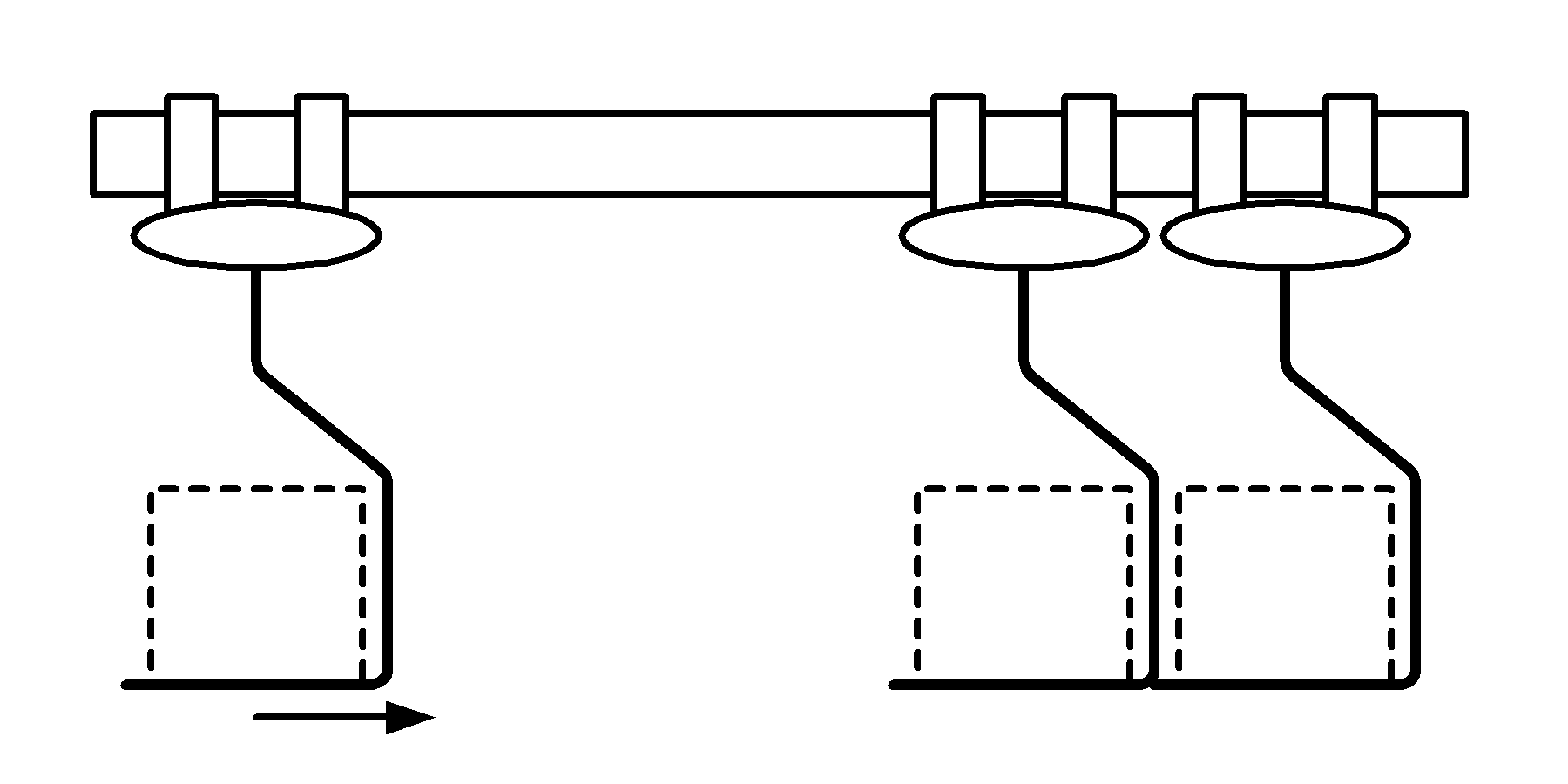
Stationary or movable arms that deflect, push, or pull a product to desired destination
Since they do not come in contact with the conveyor, they can be used with almost any flat surface conveyor
Usually hydraulically or pneumatically operated, but also can be motor driven
Simple and low cost
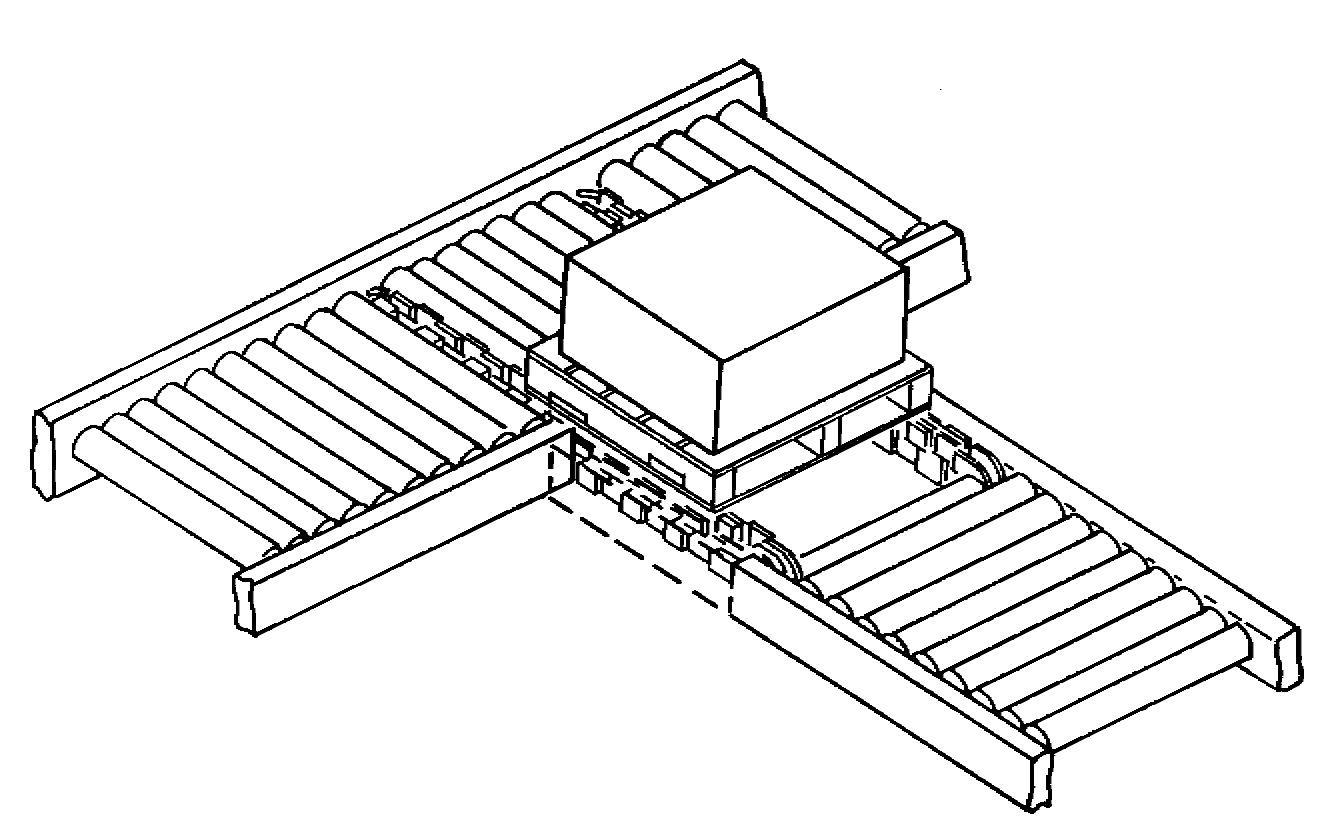
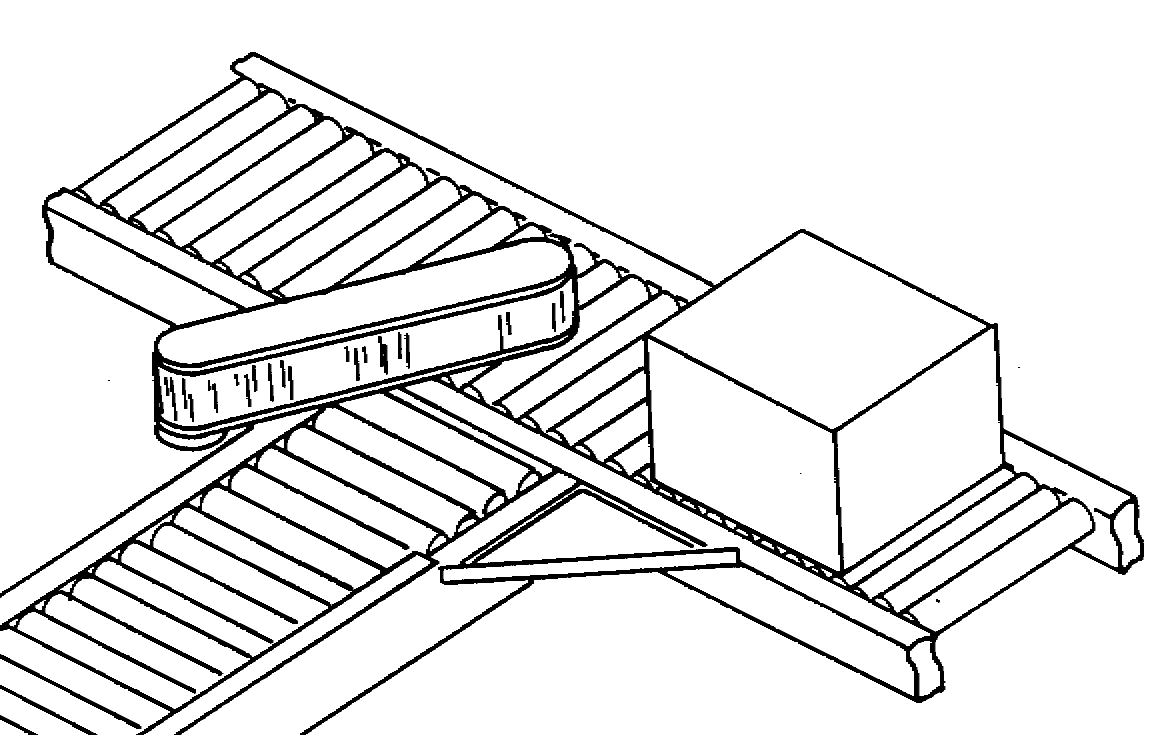
One or more rows of powered rollers or wheels or chains that pop up above surface of conveyor to lift product and guide it off conveyor at an angle; wheels are lowered when products not required to be diverted
Only capable of sorting flat-bottomed items
Pop-up rollers are generally faster than pop-up wheels
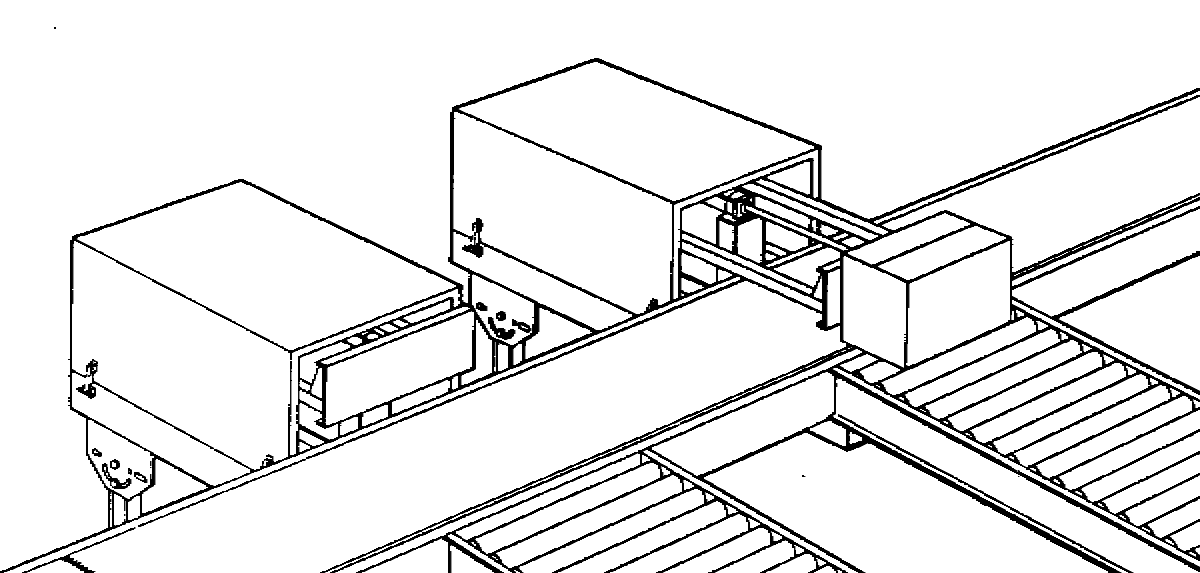
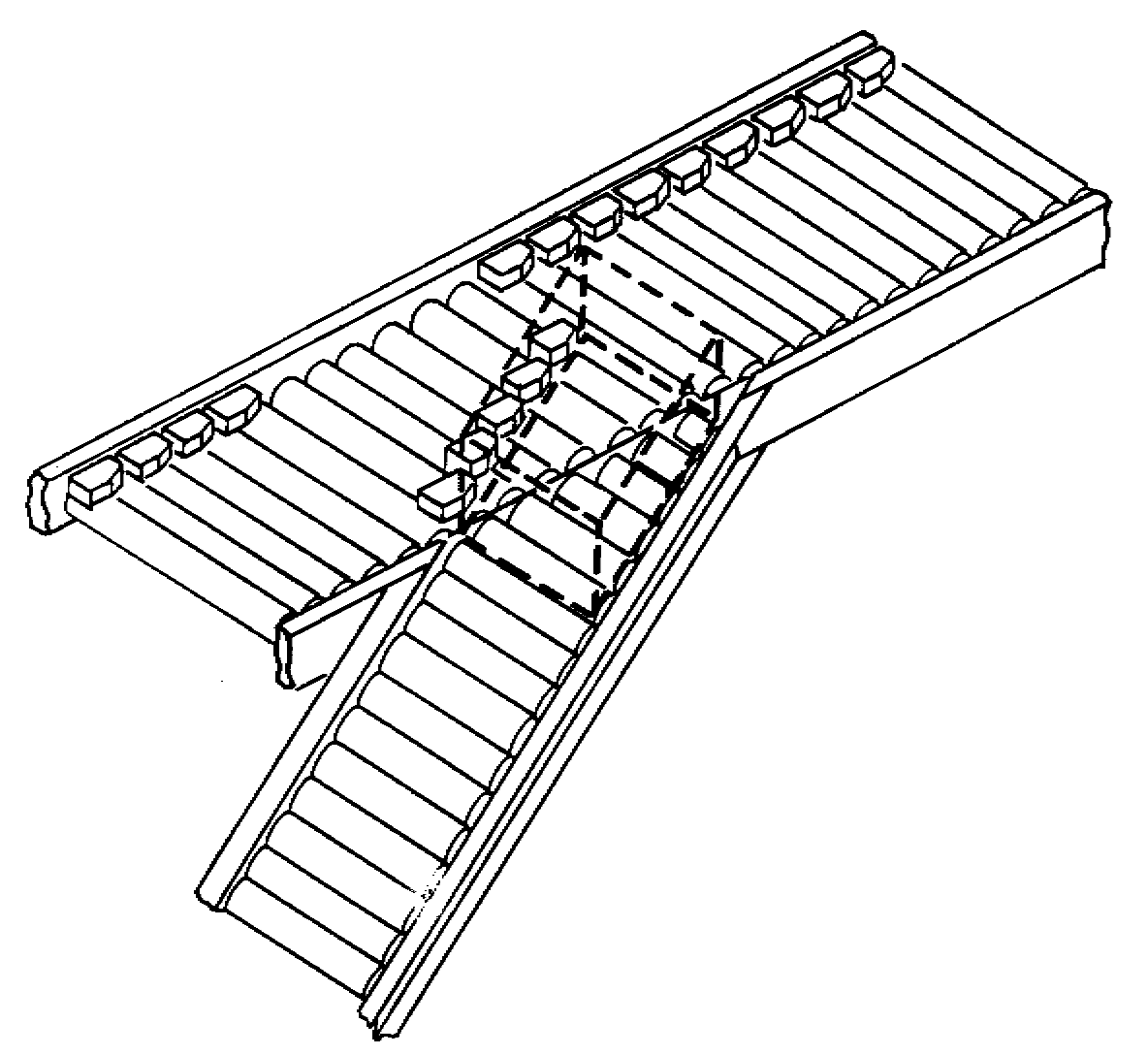 Sliding
shoe sorter (a.k.a. moving slat sorter) uses series of diverter slats that slide across
the horizontal surface to engage product and guide it off conveyor
Sliding
shoe sorter (a.k.a. moving slat sorter) uses series of diverter slats that slide across
the horizontal surface to engage product and guide it off conveyor
Slats move from side to side as product flows in order to divert the product to either side
Gentle and gradual handling of products
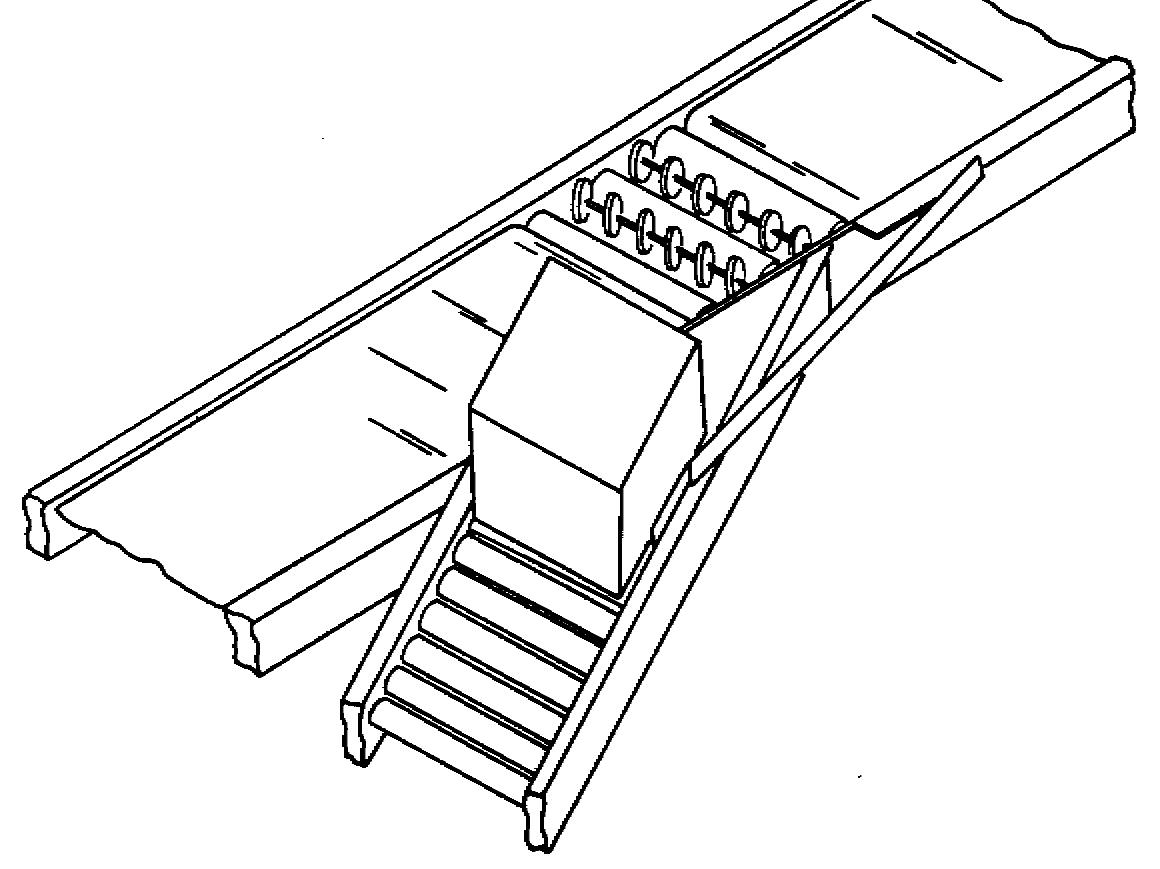
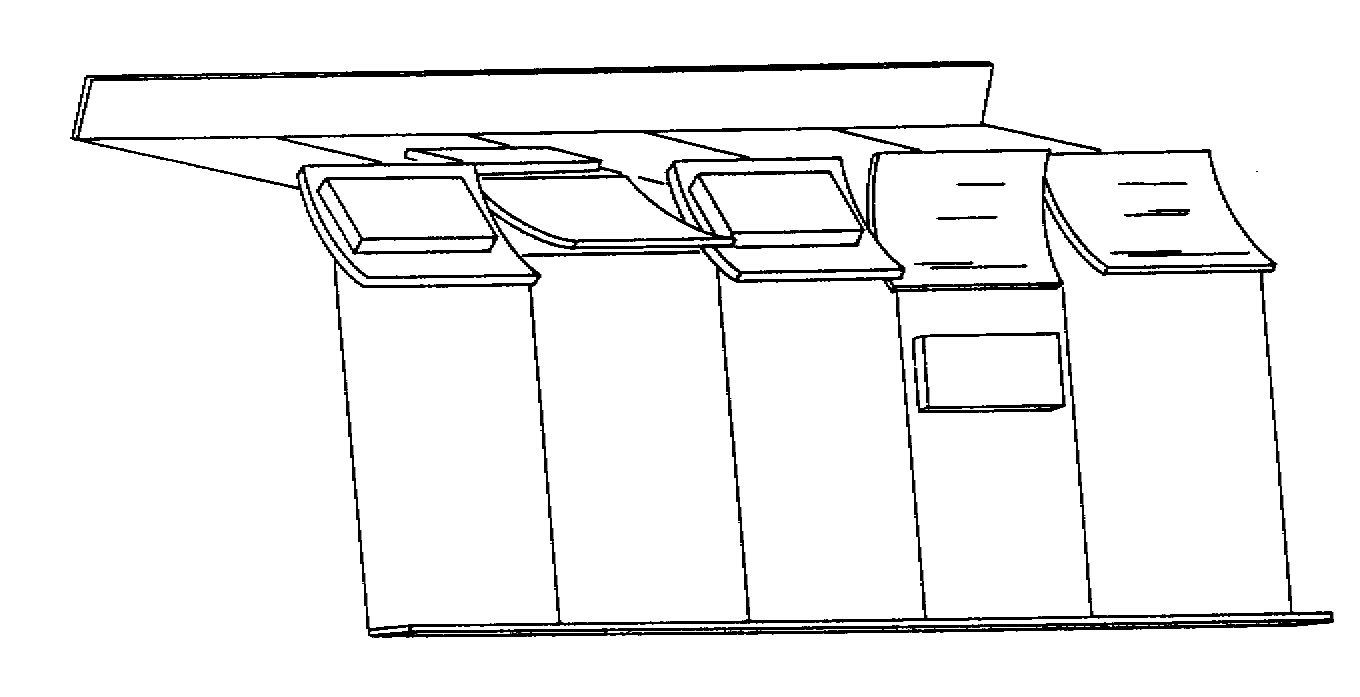 Trays or slats provide combined sorting mechanism and product transporter
Trays or slats provide combined sorting mechanism and product transporter
Can accommodate elevation changes
Tilt tray sorters usually designed in continuous loops with a compact layout and recirculation of products not sorted the first time
Tilt slat sorters carry products on flat-surface slat conveyor and can handle wider
variety of products compared to tilt tray
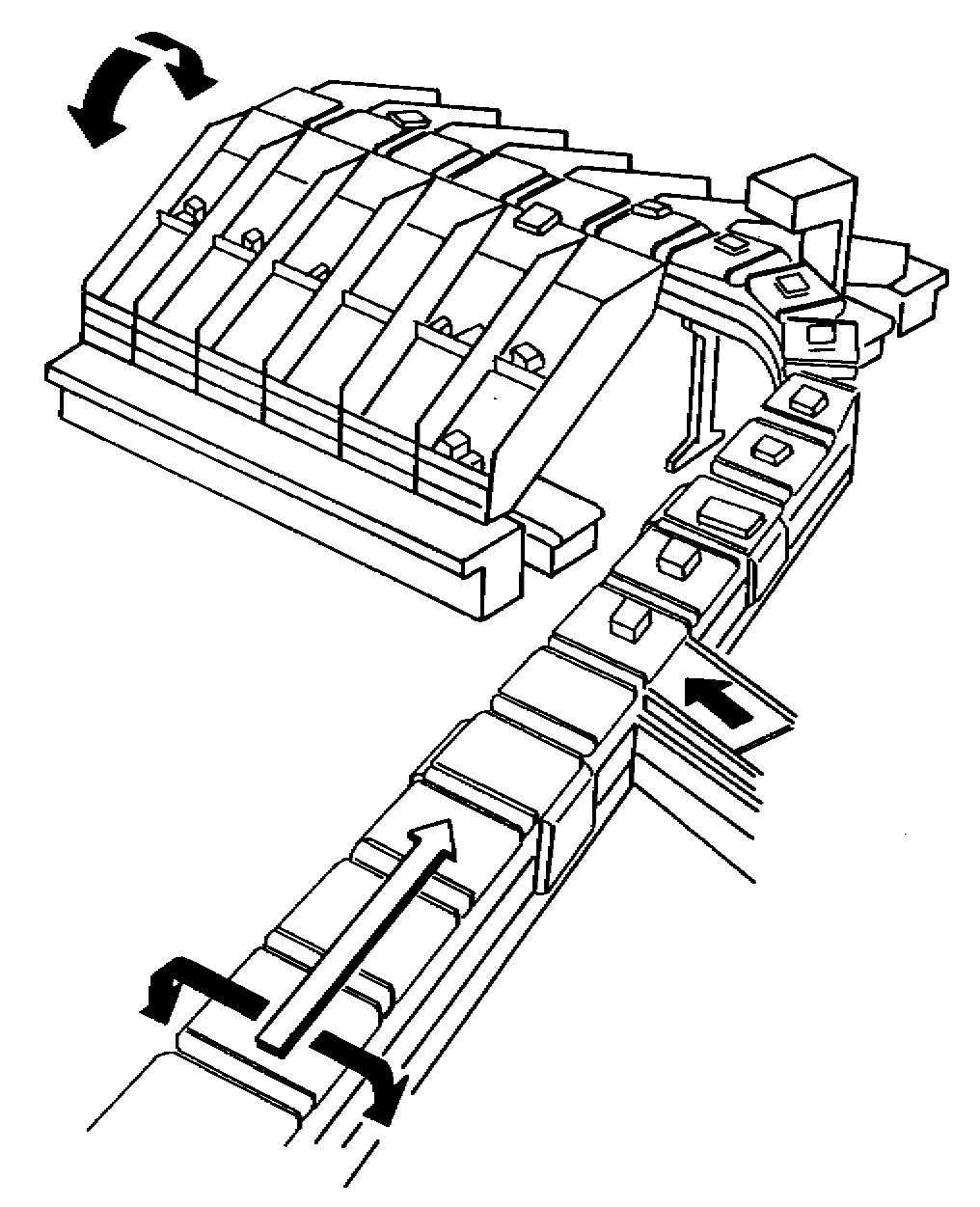 Either continuous loop, where individual carriages are linked together to
form an endless loop, or train style (asynchronous), where a small number of carriers tied
together with potential for several trains running track simultaneously
Either continuous loop, where individual carriages are linked together to
form an endless loop, or train style (asynchronous), where a small number of carriers tied
together with potential for several trains running track simultaneously
Each carriage equipped with small belt conveyor, called the cell, that is mounted perpendicular to direction of travel of loop and discharges product at appropriate destination
Automatically separates single line of products into multiple in-line discharge lines
| Top | Back to MHI | Transport | Positioning | Unit Load Formation | Storage | Identification & Control |